The Different German Prepositions for Woher, Wo and Wohin

Different prepositions in German.
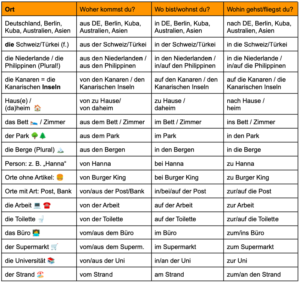
I admit, the German language is quite complex regarding its many prepositions with different uses depending on the questions woher, wo or wohin. In this post, I’m going to offer you a table with the most common places as well as some rules.
I. General Rules
1. Woher?
When we come from a place, we use von or aus. The difference between these two prepositions is the following: We use aus when we come from inside a place, this includes countries and cities (because you have been inside them). Von means we are coming from being near a place, or from a flat place like a square (see point II.2.).
2. Wohin?
When we say where we go (to), we also have 2 main prepositions: nach and zu. The general rule is we use nach with places without articles (countries, cities, islands, regions) and zu for places with article (die Post/der Arzt) as well as people (Sarah) and places with concrete names (McDonald’s, Zara…).
The only exception is the term Hause: We say ich gehe nach Hause (to go home) but ich bin zu Hause (to be [at] home).
II. More Detailed Rules
1. Countries, cities, regions (for islands, click here)
The same rules apply for countries, cities and regions:
- Woher kommst du? – Ich komme aus Österreich/Lissabon/Andalusien.
- Wo bist du? – Ich bin in Schweden/Helsinki/Kalabrien.
- Wohin fährst du? – Ich fahre nach Liechtenstein/Hamburg/Sibirien.
Only if the country or region has an article (die Schweiz/Türkei/Ukraine/ Normandie/Toskana, die Niederlande/USA, der Irak/Iran/Jemen), it takes in (+ Akkusativ) also with wohin: Wohin fährst du? – Ich fahre in die Tschechische Republik/Bretagne. (If you ask wo, in takes dative case.)
2. Places with a (big) surface
Like in English, in German we consider to be on (auf) a flat place or open space such as: der Platz, der Balkon, die Terrasse, das Land/Feld/Dorf (the same concept applies for islands) and also the toilet is a place we sit on!
- Woher kommst du?– Ich komme vom Barbarossaplatz/Balkon/der Terrasse/Toilette.
- Wo bist du? – Ich bin auf dem Platz/Balkon/der Toilette/Arbeit.
- Wohin fährst du?– Ich fahre zum Alexanderplatz/gehe auf die Toilette/den Balkon.
3. People(‘s places)
We have special prepositions expressing that you are in/at → bei, or go to someone’s place → zu. It may be a simple given name (Hanna) or a profession (Frisör).
- Woher kommst du? – Ich komme von Hanna/vom Frisör/Arzt.
- Wo bist du? – Ich bin bei Hanna/beim Frisör/Arzt.
- Wohin fährst du? – Ich fahre zu Hanna/zum Frisör/Arzt.
4. Places you go to(wards) or enter (inside)
In German, we distinguish between going to (direction) or being near a place (e.g. when I meet someone at the door, or there’s a busstop…) → zu. The other aspect is entering or being inside a place (e.g. when I meet someone inside, or I want to buy something) → in. When we come from near a place → von, when we get out of the inside → aus.
- Woher kommst du? – Ich komme aus dem Krankenhaus/aus der Post. (I’ve been inside.) / Ich komme vom Krankenhaus/von der Post.
- Wo bist du? – Ich bin im Krankenhaus/in (or: bei) der Post (I am inside). / Ich bin am Krankenhause/an der Post (very near/next to the post office).
- Wohin gehst du? – Ich gehe zur Post (direction). / Ich gehe in die Post (I go inside because want to buy/send something).
The same happens with types of water (Meer/Strand, See, Fluss): direction → zu, staying near/next to it → an:
Wohin gehst du? – Ich gehe zum Strand (direction). / Ich gehe an den Strand (= I’m planning to stay on the beach).
Wo? oder Wohin?
Then you have learnt the different German prepositions.





























