Questions in German Grammar

Questions in German, also known as interrogative sentences, are used to get information about something. There are two different kinds of questions: closed questions, also called yes/no questions or Entscheidungsfragen in German; and open questions, also called w-questions or Ergänzungsfragen in German. The structure of open and closed questions is different.
Questions in German Grammar
They known as interrogative sentences, are used to get information about something. There are two different kinds of questions: closed questions, also called yes/no questions or Entscheidungsfragen in German; and open questions, also called w-questions or Ergänzungsfragen in German. The structure of open and closed questions is different.
Closed Questions
Closed questions or, Entscheidungsfragen in German, are questions that we can answer with the words “yes” or “no”. In these questions, the finite verb is in the first position. The subject follows in the second position. The rest of the sentence (object, time, place, etc.) come in the same order as they would in a main clause.
Example: Habe ich dir das Buch gegeben?
Open Questions
Open questions, or Ergänzungsfragen in German, are questions that use an interrogative pronoun or question word. We cannot answer open questions with “yes” or “no”. The interrogative pronoun comes at the beginning of the sentence. After that comes the finite verb, and then the rest of the sentence. The part of the sentence that we’re asking about is replaced by the interrogative pronoun.
Example: Wann habe ich dir das Buch gegeben?
(Gestern habe ich dir das Buch gegeben.) .
If we’re asking about an object with a preposition, the preposition comes before the question word.
Example: Mit wem gehst du ins Kino? .
Für wen ist das Geschenk?
If we’re asking about the subject, the finite verb takes the third person singular.
Example: Wer hat dir das Buch gegeben?
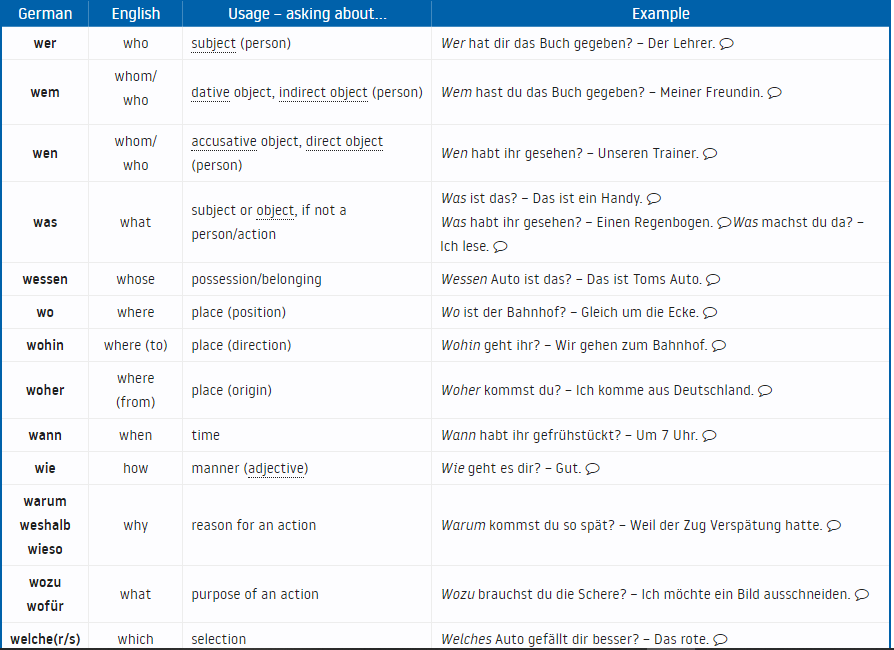
Typical Question Words
The chart below provides an overview of typical question words in German and their usage along with English translations and examples.
Questions with Wo + Preposition: woran, wofür, womit
If in English we often use what with prepositions in questions. In standard German, we contract wo and the preposition to make wo-compouns. We can also use prepositions with was, but this is very colloquial and casual.
Example: Mit was kann ich helfen?
better: Womit kann ich helfen?
If the preposition begins with a vowel, we add an r between wo and the preposition.
Example: An was denkst du?
better: Woran denkst du?
Indirect Questions
We use indirect questions in dependent clauses.
Example: Ich weiß nicht, was das ist.
At last you can improve your German online with Learning German App.




























